WHAT IS THE Largest Ports IN Netherlands? The Netherlands has long been recognized as Europe’s maritime gateway. With its strategic location at the mouth of major rivers like the Rhine, Maas, and Scheldt, the country has developed some of the busiest and most advanced ports in the world. These ports not only serve Dutch businesses but also act as critical hubs for European and global trade. For Chinese exporters, the Netherlands is often the first point of entry into Europe, making it a vital partner in international logistics.
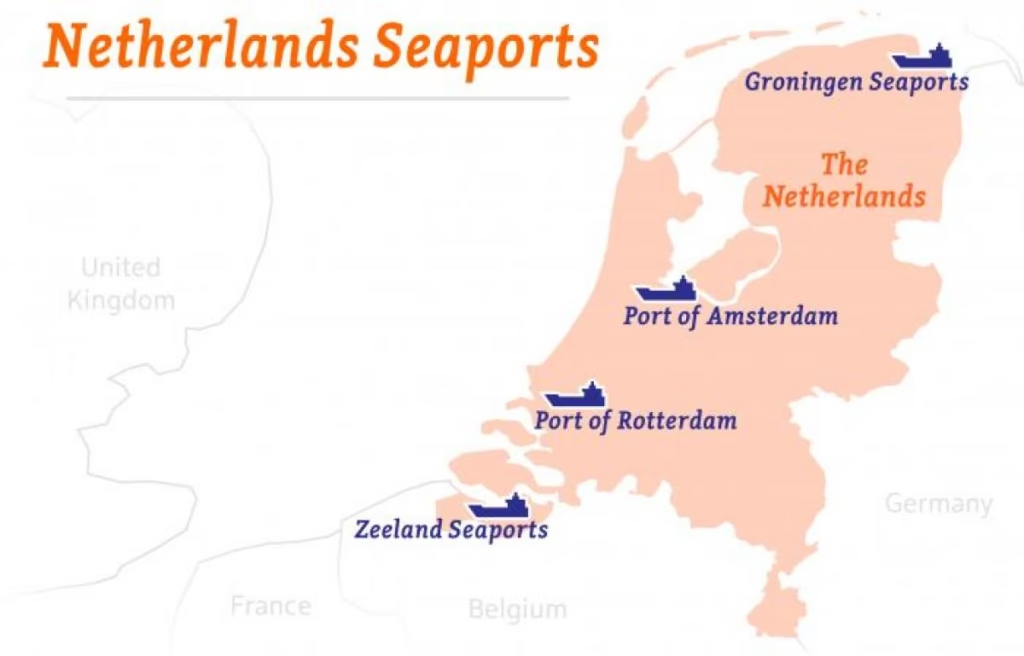
The Largest Ports in the Netherlands
The Netherlands is home to more than 20 significant ports, but a few stand out as global leaders in cargo handling and logistics.
1. Port of Rotterdam
- Europe’s largest seaport and the 10th busiest in the world.
- Handles over 440 million tonnes of cargo annually.
- Specializes in containers, crude oil, chemicals, and bulk cargo.
- Known for its advanced digital logistics systems and sustainability initiatives.
2. Port of Amsterdam
- The second-largest port in the Netherlands.
- Strong in energy products, agribulk, and general cargo.
- Plays a growing role in cruise tourism and renewable energy logistics.
3. Groningen Seaports (Eemshaven & Delfzijl)
- Important for offshore wind energy and heavy industry.
- Increasingly used for project cargo and specialized shipments.
4. Vlissingen & Terneuzen (North Sea Port)
- Located near Belgium, these ports are crucial for bulk cargo and industrial raw materials.
Together, Dutch ports handle over 600 million tonnes of cargo annually, making the Netherlands one of the top 10 global trading nations.
China–Netherlands Trade Relations
China and the Netherlands maintain a robust trade partnership.
- In 2024, Dutch exports to China reached US$22.24 billion, with machinery, electronics, and medical equipment leading the way.
- Imports from China include electronics, textiles, and consumer goods, making China one of the Netherlands’ largest trading partners.
- In June 2025, Dutch exports to China grew by 13% year-on-year, reaching €2.54 billion.
This trade is facilitated by the Netherlands’ ports, which serve as entry points for Chinese goods destined for the wider European Union.
Major E-Commerce Platforms in the Netherlands
The Netherlands has a thriving e-commerce market, valued at over €34 billion in 2024. Local platforms dominate, though international players are also present.
- Bol.com – The largest Dutch online marketplace, often called the “Amazon of the Netherlands.”
- Marktplaats.nl – A leading second-hand and consumer-to-consumer platform.
- Amazon.nl – Present but ranks behind local players.
- Coolblue – Popular for electronics and home appliances.
- Wehkamp – Strong in fashion and lifestyle products.
Interestingly, platforms like AliExpress, Shein, and Temu are growing but are not yet in the top 10. This shows Dutch consumers’ preference for local and trusted platforms.
How to Ship Goods from China to the Netherlands
There are several ways to transport goods from China to the Netherlands, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
1. Sea Freight
- FCL (Full Container Load): Best for large shipments. Cost-effective per unit, but slower (30–40 days).
- LCL (Less than Container Load): Suitable for smaller shipments. Flexible but involves consolidation delays.
- Pros: Cheapest for bulk cargo, environmentally friendly.
- Cons: Long transit time, potential port congestion.
2. Air Freight
- Transit time: 5–10 days.
- Pros: Fast, reliable, ideal for high-value or urgent goods.
- Cons: Expensive, limited by weight and volume.
3. Rail Freight (China–Europe Railway)
- Transit time: 18–22 days.
- Pros: Faster than sea, cheaper than air, stable schedules.
- Cons: Limited capacity, geopolitical risks, higher cost than sea.
4. Express Courier (DHL, FedEx, UPS)
- Transit time: 3–7 days.
- Pros: Door-to-door service, customs handled.
- Cons: High cost, suitable only for small parcels.
5. Tax-Free Routes (Special Logistics Providers)
- Some providers offer tax-prepaid or bonded warehouse solutions.
- Pros: Simplifies customs clearance.
- Cons: May involve higher service fees.
Case Example: Electronics Shipping
A Shenzhen-based electronics manufacturer exporting to Dutch e-commerce sellers might choose:
- Air freight for urgent product launches.
- Rail freight for mid-sized shipments balancing speed and cost.
- Sea freight for large seasonal stock replenishments.
This multi-modal approach ensures flexibility and cost efficiency.
Import Duties and Taxes When Shipping from China to the Netherlands
When importing goods from China into the Netherlands, businesses must consider not only the shipping costs but also the customs duties, VAT, and other possible charges. These fees significantly affect the total landed cost of products.
1. Customs Duties (Import Tariffs)
- The Netherlands, as an EU member state, applies the EU Common Customs Tariff (CCT).
- Duty rates depend on the HS (Harmonized System) or TARIC code of the product.
- Examples:
- Electronics (e.g., laptops, smartphones): often 0–5% duty.
- Textiles and apparel: typically 12–17% duty.
- Automotive parts: around 4–10% duty.
- Importers must classify their goods correctly to avoid penalties or delays.
2. Value Added Tax (VAT)
- Standard VAT rate in the Netherlands: 21%.
- Reduced VAT rate: 9% (applies to certain goods like food, books, and medicines).
- VAT is calculated on the CIF value (Cost + Insurance + Freight) plus customs duty.
- Example:
- If a shipment of textiles worth €10,000 has 12% duty (€1,200), the VAT base is €11,200.
- VAT (21%) = €2,352.
- Total tax burden = €1,200 (duty) + €2,352 (VAT) = €3,552.
3. Excise Duties
- Some products (alcohol, tobacco, energy products) are subject to excise duties in addition to VAT and customs duty.
4. Other Fees
- Customs clearance fees: charged by freight forwarders or customs brokers.
- Anti-dumping duties: may apply to certain categories (e.g., steel, solar panels) depending on EU trade policies.
5. Practical Tips for Importers
- Always check the TARIC database before shipping to confirm the exact duty rate.
- Consider using bonded warehouses in the Netherlands to defer VAT payments until goods are sold.
- For e-commerce sellers, the IOSS (Import One-Stop Shop) scheme simplifies VAT collection for shipments under €150.
Example Case
A Dutch retailer imports 1,000 pairs of shoes from China valued at €20,000.
- Customs duty (16%) = €3,200.
- VAT base = €23,200.
- VAT (21%) = €4,872.
- Total taxes = €8,072, making the landed cost €28,072.
This example shows why accurate cost calculation is essential for pricing and profitability.
Temu vs. Shein: Which App is Safer
By langxu freight | Updated: 2026 The battle for the top spot in the ultra-fast…
Mastering the Ocean Bill of Lading
In the fast-paced world of international logistics, cargo moves across oceans, but paperwork rules the…
e-commerce How to Secure Your Supply Chain and Amplify Your Brand
Your shop is growing. The adrenaline of the first few sales has settled into a…



Pingback: Italy Major Ports and a Practical Guide to Shipping from China
Your writing is like a breath of fresh air in the often stale world of online content. Your unique perspective and engaging style set you apart from the crowd. Thank you for sharing your talents with us.