WHAT IS DDU WHILE SHIPPING FROM CHINA? Your Complete Guide to Delivery Duty Unpaid, Understand the intricacies of DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid) Incoterms in global trade. Learn about the responsibilities, risks, and costs involved for both buyers and sellers, and how it compares with other Incoterms.
DDU brief introduction
DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid), an older term in the Incoterms lineup, sets out a deal in which the seller covers transport costs and all risks involved in transferring the goods. However, the tab for import duties, taxes, and extra delivery costs inside the destination country goes on the buyer’s shoulders.
That’s quite the opposite of DDP (delivery duty paid), where the seller has to cover every cost of transporting the goods to the buyer’s doorstep.
DDU was phased out in the 2010 and 2020 Incoterms revisions but was soon replaced by DAP (Delivery-at-Place). However, DDU is still often seen in shipping and transport contracts.
So, whether you’re a seller or a buyer, you must learn about the latest DDU Incoterms to stay compliant and reduce your delivery, tax, and destination charge risks. A perfectly executed transition from DDU to DAP can put your business in a better position for secure global dealings.
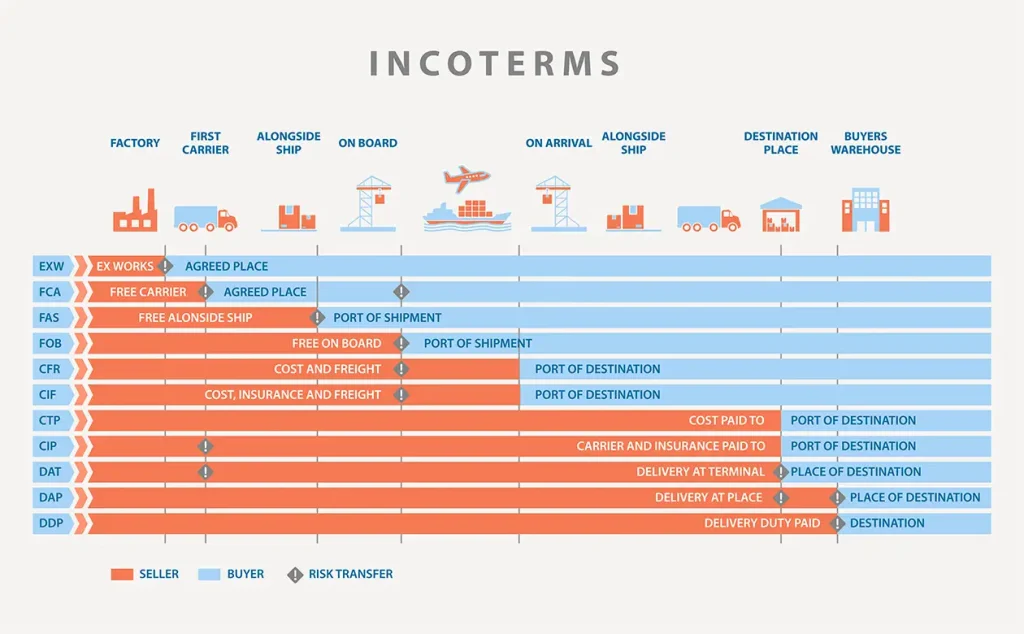
What Are Incoterms?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, consist of 11 rules from the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They define who’s responsible for what in international transactions.
Incoterms are primarily divided into two categories:
Universal Transport Modes: Incoterms like EXW, FCA, CPT, CIP, DAP, DPU, and DDP fit any transport method.
Sea and Waterway Specific: Incoterms such as FAS, FOB, CFR, and CIF are meant for sea and river shipments, not containerized freight.
Key Incoterms 2024 Focus Areas
The recent Incoterms 2020 focus on:
Delivery: Marks the moment risk and duty shift from seller to buyer.
Transportation: Details who manages and pays for shipping.
Documentation: Clarifies who is responsible for getting the shipping papers and handling customs.
Insurance: Outlines who must insure the goods, crucial for risk management during shipping.
Using Incoterms in contracts clarifies everyone’s duties, responsibilities, and cost division. This eventually helps prevent potential disputes and misunderstandings in global trade.
What is DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid)
DDU, or Delivered Duty Unpaid, is a shipping term used in international trade to define how sellers and buyers share duties and costs. If you’re into global trade, you must know what sellers and buyers do in DDU to avoid any surprises.
For the Seller
- The seller packs the goods and handles all the paperwork needed to export them.
- They pay to transport the goods all the way to a specific place in the buyer’s country but not beyond that.
- They also provide the documents necessary for the goods to leave the country.
For the Buyer
- The buyer takes over everything once the goods reach the specified place.
- They are responsible for paying any customs duties and taxes needed to bring the goods into their country.
- If the goods need to be moved further, like to the buyer’s store or warehouse, that also goes on the buyer’s plate.
As you can see, DDU allows buyers to control the import process and frees up sellers from dealing with the destination country’s regulations. However, it does put buyers on the spot to pay the cost of duties and taxes once the goods arrive in their country.

Key Differences Between DDU and Other Incoterms
Timely decision-making is the key to international shipping. To be a pro player in this industry, you must know how DDU stands apart from other Incoterms.
But this can be difficult to do, considering the wide range of terms available.
For your ease, we have compared DDU differences with the three significant Incoterms: DDP, DAP, and LDP (Landed-Duty Paid).
- DDU vs. DDP
Under DDU, the buyer is responsible for covering import duties, taxes, and extra delivery costs in their country. Comparatively, DDP shifts all responsibilities, including risks, transport costs, and customs duties, to the seller until the buyer receives the goods.
- DDU vs. DAP
As you know, DAP replaced DDU in 2010. So, both terms are essentially the same.
With DAP, the seller pays to transport the goods to the chosen destination. The buyer then handles customs clearance and taxes. That’s exactly what happens in DDU.
- DDU vs. LDP
Compared to DDU, LDP simplifies things for the buyer. The seller takes on all expenses, including transport, customs clearance, and taxes. This makes LDP a more buyer-centric option.
The US has strict customs regulations for the buyers. So, if you plan to export goods to such countries, you should choose DDU as your priority.
What is the difference between DDU and DDP incoterm?
DDU and DDP are broad terms with different terms and conditions involved for sellers and buyers. As a global trader, you should understand these Incoterms in detail to ensure everything goes smoothly.
Let’s compare DDU and DDP Incoterms:
Responsibilities and Costs:
- DDU: In DDU, the buyer is responsible for import duties, taxes, and all delivery-related costs within the destination country. Not only that, but they also have to bear extra expenses like customs charges and additional fees for brokerage, storage, or late payments.
- DDP:On the other hand, in DDP, the seller bears the transport costs, customs duties, and any other risks until the goods are handed over to the buyer. This means as a seller, you will have to take care of Goods and Services Tax (GST), customs clearance, and VAT.
In some cases, the seller and the buyer agree on a mutual decision in which the seller doesn’t have to pay all these costs. So, make sure to communicate with the buyer if you want to choose DDP but don’t want to pay the taxes and costs.
Advantages for Different Parties
DDU is often the go-to option for companies that manage a heavy load of shipments on a daily basis. This option offers impeccable flexibility, empowering businesses to handle deliveries without going out of budget.
Meanwhile, DDP is popular among retailers and e-commerce businesses. This Incoterm simplifies shipping, lowers risks, and enhances the customer experience with transparent finances. The result is seamless delivery and easy fee management.
Risk and Compliance
With DDU, the risk shifts to the buyer once the goods arrive in the destination country. They have to handle all sorts of paperwork like import documentation and licenses.
However, DDP requires the seller to deal with customs clearance and paperwork. Not only that, but as a seller, you’d also have to handle all the incurred costs beforehand, including duties and taxes.
This ensures that the shipments are successfully delivered instead of getting left behind due to surprise fees.

DDU vs DDP: What is Cheaper?
If you want a cost-effective option, you should weigh various factors to decide on DDU and DDP. Here are some things to consider to make an informed choice:
Understanding of Import Regulations
If you’re familiar with the import rules and customs of the destination country, using DDU could give you more control. It can also be more cost-effective, as you will be in charge of handling import duties and taxes.
If you can’t get your head around customs processes, you should choose DDP to avoid any potential mistakes. However, it might be more expensive upfront since the seller covers all customs duties and taxes.
Breakdown of Costs and Fees
In DDU, the seller covers the transport costs to the agreed-upon destination, and the buyer covers customs duties, import tariffs, and additional charges.
When it comes to DDP, the seller covers all transport costs, customs duties, import tariffs, and any extra fees until the buyer receives the goods.
So, DDU vs. DDP, what is best for you in terms of cost? Your decision should depend on how well you can handle customs procedures, costs, and risks of international shipping.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Choosing DDU
The major advantage of DDU is that you will be in charge. Most buyers prefer DDU because it gives them more control over the entire shipping process.
So, if you’re a buyer, DDU will let you pick your carrier and the logistics using your own contacts and preferences.
However, there are some downsides that you must watch out for, such as:
- Unexpected Costs: You might be surprised by some unexpected fees when you receive your shipment. It could be additional duties and taxes, which may exceed your original budget.
- Dealing with Customs: You’d have to handle all the paperwork required to bring goods into the country. This means you may have to study the local import rules, which can be pretty complex.
So, your decision about whether to choose DDU depends on your budget, preferences, and shipping needs.
Hopefully, now you might be feeling more confident about your understanding of DDU and how it fits into international trade. As a global trader, you should know how DDU compares with other Incoterms in regard to the shipping duties, risks, and costs involved.
Remember, DDU has its pros and cons, which you should evaluate before making any decision. There might be another Intercom that fits your shipping needs, so always keep your options open.
Temu vs. Shein: Which App is Safer
By langxu freight | Updated: 2026 The battle for the top spot in the ultra-fast…
Mastering the Ocean Bill of Lading
In the fast-paced world of international logistics, cargo moves across oceans, but paperwork rules the…
e-commerce How to Secure Your Supply Chain and Amplify Your Brand
Your shop is growing. The adrenaline of the first few sales has settled into a…