Discover how Mercado Livre is shaping Brazil’s e-commerce landscape in 2025, leading the charge in Latin America’s digital marketplace evolution.
Market Background: A Booming Brazilian E-Commerce Landscape
Brazil’s e-commerce market is on an extraordinary growth trajectory. In 2025, the sector is projected to reach R$59.07 billion (about $11.5 billion USD) in revenue, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.04% through 2030. This surge is driven by rising internet penetration, a growing middle class, and the lasting impact of the pandemic which accelerated digital adoption. The country boasts over 100 million online shoppers, and mobile commerce accounts for about 60% of all online purchases.
Notably, Brazil’s e-commerce platform traffic reflects this dynamism – the top platforms collectively command around 57.5% of total visits, underscoring a highly concentrated market. Mercado Livre (known as Mercado Libre in most of Latin America) sits at the apex of this market, maintaining its position as the most visited e-commerce portal in the country. Its dominance is further evidenced by its leading market share (around 15.3% of total visits in the past year), though competitors like Shopee, Amazon Brasil, and others are nipping at its heels. Overall, Brazil’s e-commerce industry is characterized by robust growth, fierce competition, and a rapidly evolving digital ecosystem – setting the stage for an in-depth analysis of Mercado Livre’s performance in this vibrant market.
Mercado Livre’s 2025 Performance: A Year of Strong Growth and Strategic Expansion
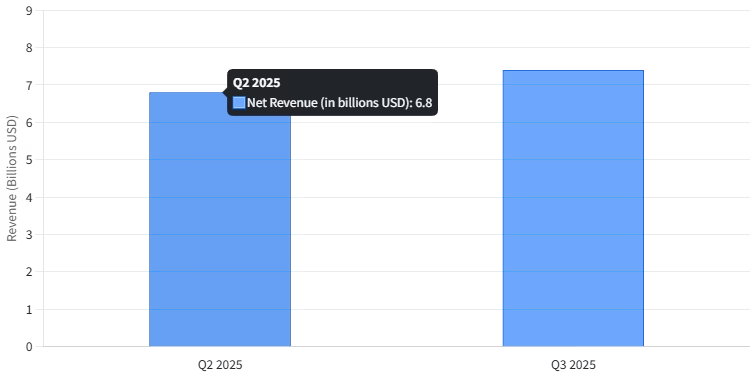
Revenue and Profit Growth: Mercado Livre delivered exceptional financial results in 2025, continuing a multi-year streak of robust expansion. The company’s full-year revenue (across commerce and fintech) grew significantly, driven by strong performance in Brazil. In Q2 2025, Mercado Livre’s net revenue reached $6.8 billion, a 35% year-over-year increase. This momentum accelerated into Q3 2025, with net revenue soaring to $7.4 billion, up 39% YoY – the 27th consecutive quarter of growth exceeding 30%. Net income in Q3 2025 also climbed 30% YoY to $724 million, reflecting improved operational leverage. These figures underscore Mercado Livre’s ability to translate market growth into bottom-line results.
A key driver was the commerce business, which generated $4.2 billion in Q3 revenue (up 33% YoY), as well as the fintech arm (Mercado Pago) which contributed $3.2 billion in Q3 revenue (up 49% YoY). The company’s gross merchandise volume (GMV) – a critical metric for e-commerce – also surged. In Q3, GMV hit $16.5 billion, a 28% YoY increase in USD terms (or 35% on a FX-neutral basis).
This growth indicates that Mercado Livre is not only attracting more buyers but also convincing them to spend more on its platform. In Brazil specifically, GMV grew 34% YoY, and the number of items sold rose 42% YoY. Such figures highlight the strength of Mercado Livre’s core commerce operations in its largest market.
Mercado Livre’s Net Revenue Growth in Q2 and Q3 2025
User Growth and Market Share: Mercado Livre’s 2025 performance was also marked by rapid user acquisition and deeper market penetration in Brazil. The number of unique buyers on its platform across the region reached nearly 77 million in Q3 2025, a 26% YoY increase. In Brazil, buyer growth was even more impressive – unique buyers grew 29% YoY, the fastest pace since early 2021. This surge in customers translated into record quarterly additions of new buyers in the country. As a result, Mercado Livre solidified its leading market position. By late 2025, Mercado Livre commanded roughly 15.3% of Brazil’s total e-commerce platform visits, placing it well ahead of rivals.
This market share edge, however, was hard-won. The company had to invest aggressively in free shipping and other incentives to attract and retain buyers in the face of stiff competition. The payoff was evident in conversion rates hitting record highs and improved customer retention. Mercado Livre’s success in drawing users also bled into its fintech ecosystem. Mercado Pago’s monthly active users (MAU) rose 29% YoY to 72 million in Q3 2025, indicating that many e-commerce shoppers are also using the platform’s financial services. This cross-pollination of users between commerce and fintech is a hallmark of Mercado Livre’s strategy and a key advantage in the market.
Core Business Lines Development: Mercado Livre’s 2025 results reflect the strength of its two main pillars – e-commerce and fintech – and the synergies between them. In e-commerce, the company continued to invest heavily in its logistics and fulfillment network to enhance customer experience. By Q3 2025, Mercado Livre had increased its fulfillment center capacity by 41% YoY. This investment enabled faster delivery times and greater reliability, which in turn boosted buyer satisfaction and conversion.
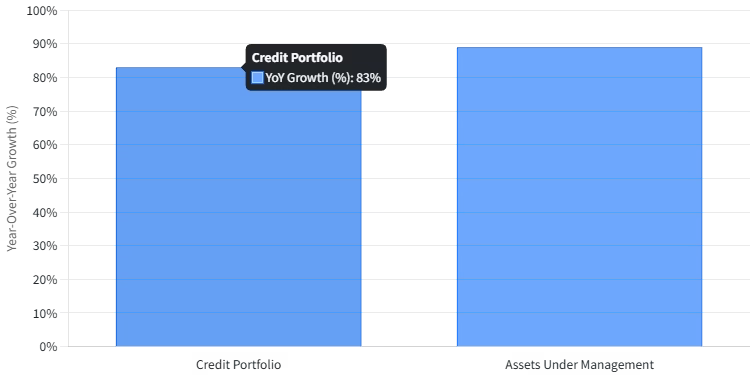
In Brazil, for instance, the company leveraged its logistics to offer same-day or next-day delivery in more regions, a capability that competitors struggle to match at scale. These efforts helped drive the 42% YoY jump in items sold in Brazil. The company also saw strong performance in Mexico and Argentina, indicating that its logistics playbook is effective across its key markets. Meanwhile, Mercado Livre’s fintech arm, Mercado Pago, had a breakout year. It is on track to become one of Latin America’s largest digital banks. In Q3 2025, Mercado Pago’s credit portfolio surged 83% YoY to $11.0 billion, and its total assets under management nearly doubled, growing 89% YoY to $15.1 billion.
This expansion was fueled by Mercado Pago’s introduction of a credit card in Brazil, which quickly became the most used credit card on the platform. The card’s success (with over 50% of its total payment volume coming from off-platform transactions in Brazil) demonstrates the broad utility of Mercado Pago’s financial offerings. Additionally, Mercado Pago’s digital wallet and payment solutions are increasingly used by small merchants and consumers, deepening Mercado Livre’s ecosystem engagement. The advertising business (Mercado Ads) also showed strong growth, with revenue jumping 56% YoY in Q3 2025.
Mercado Ads, which combines first-party data with off-platform inventory, is becoming a significant profit center and a way for merchants to reach more customers. Overall, Mercado Livre’s core business lines in 2025 were firing on all cylinders – e-commerce growth was fueled by logistics investments and user acquisition, while fintech growth was driven by innovative financial products and expanding acceptance. The synergy between these segments (e.g. using commerce data to underwrite loans, or using Mercado Pago to facilitate online purchases) creates a virtuous cycle that strengthens Mercado Livre’s competitive position.
YoY Growth of Mercado Pago’s Fintech Metrics in Q3 2025
Competitive Landscape: Dominance Amidst Intensifying Rivalry
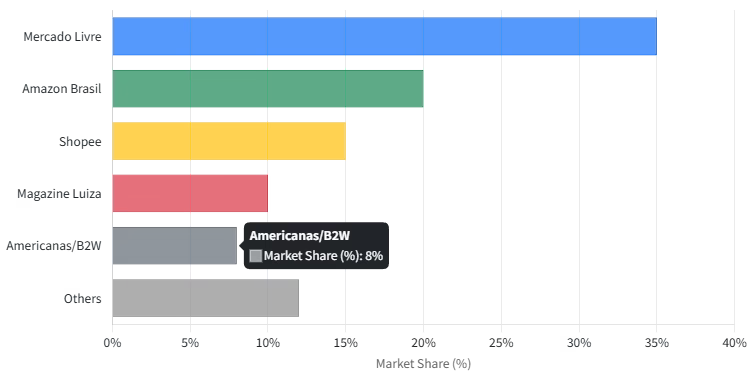
Mercado Livre’s commanding market share in Brazil does not mean it faces an easy road. In fact, the competitive landscape is fierce and constantly evolving. Domestic and global players alike are vying for a slice of Brazil’s booming e-commerce pie. Mercado Livre’s chief rivals include a mix of international giants and regional challengers. According to the U.S. International Trade Administration, the top e-commerce portals in Brazil (by market share) are Mercado Livre (35%), Amazon Brasil (20%), Shopee (15%), Magazine Luiza (10%), and Americanas/B2W (8%).
These figures, while slightly dated, illustrate the competitive environment Mercado Livre operates in. Amazon, despite its global might, has struggled to gain significant traction in Brazil – it holds around 20% market share, but its growth has been hampered by infrastructure and cultural challenges.
A more formidable threat has emerged in the form of Shopee (owned by Sea Limited), which has rapidly captured market share by offering low prices and heavy promotions. Shopee’s aggressive tactics – including waiving seller commissions and subsidizing shipping – have forced Mercado Livre to respond by expanding free shipping offers and cutting seller fees in Brazil. This “price war” has put pressure on Mercado Livre’s margins but also underscores the intensity of the competition.
Notably, as of early 2025, Shopee’s app ranked first in Brazil by usage, followed closely by Mercado Livre. This indicates that Shopee has managed to attract a large user base, especially among price-sensitive consumers. Other competitors like Magazine Luiza (a Brazilian retail giant) and Americanas (part of the B2W group) also hold significant market share and are expanding their online and offline presence. Magazine Luiza, for example, has leveraged its physical stores to offer omnichannel experiences, while Americanas has been bolstering its online marketplace. Beyond these, new entrants are making waves.
Asian e-commerce platforms like Shein (focused on fashion) and AliExpress have gained popularity by offering a wide range of products at low prices. In 2025, Shein became one of Brazil’s top 10 e-commerce sites by traffic, and AliExpress also ranked in the top 10. Even more concerning for Mercado Livre is the rise of Temu, a Chinese ultra-low-cost platform that has rapidly gained users in Latin America by shipping directly from China. In July 2025, Temu’s traffic in Brazil was estimated at over 400 million visits, a 70% month-over-month increase, briefly overtaking the market leaders.
While Temu’s model (reliant on cross-border shipping and minimal local infrastructure) is less of a direct threat to Mercado Livre’s core business for now, its explosive growth highlights the competitive pressures in the market. In response, Mercado Livre has been doubling down on its strengths – investing in logistics and technology to differentiate its service quality from discount-focused rivals. It has also been expanding its advertising business to offer merchants another way to reach customers, thereby monetizing its traffic advantage. The competition is not just in retail; in fintech, Mercado Pago faces rivals like Nubank (a digital bank with millions of users) and other payment platforms.
However, Mercado Pago’s integration with the e-commerce ecosystem gives it an edge in convenience and data-driven financial products. In summary, Mercado Livre’s competitive position in Brazil is strong but under constant pressure. It leads in market share and customer loyalty, yet competitors are attacking from all angles – price, product assortment, and service innovation. The competitive dynamics in 2025 have pushed Mercado Livre to innovate faster and invest more, which will be critical for maintaining its lead in the years ahead.
Brazil E-commerce Market Share by Company
Strategic Assessment: Innovations, Acquisitions, and Logistics Optimization
Mercado Livre’s remarkable 2025 performance was not accidental – it was the result of deliberate strategic initiatives and investments. The company’s management has been executing on a clear playbook to expand its ecosystem and outpace rivals. Key strategies and initiatives in 2025 included:
- Aggressive Investment in Logistics and Fulfillment: Mercado Livre has long recognized that logistics excellence is a cornerstone of competitive advantage in e-commerce. In 2025, it doubled down on this strategy by significantly expanding its fulfillment network. The company announced a $6.4 billion investment in Brazil for 2025 – the largest single-country investment in its history. A major portion of this capital was earmarked for logistics infrastructure. Mercado Livre embarked on a plan to grow its fulfillment center count from 10 to 21 units by the end of 2025. These new fulfillment hubs, spanning an area equivalent to about 120 football fields, have enabled Mercado Livre to dramatically improve delivery speeds. In fact, the expansion led to a 40% increase in the number of cities that can receive same-day delivery. By cutting down delivery times and offering reliable next-day service, Mercado Livre enhances customer satisfaction and differentiates itself from competitors who may struggle with fulfillment in Brazil’s vast geography. The investment also has a cost management angle – by operating its own network, Mercado Livre can achieve economies of scale and reduce per-unit shipping costs over time. Indeed, the company reported an 8% quarter-over-quarter drop in unit shipping costs in Brazil in Q3 2025, demonstrating the efficiency gains from its logistics build-out. This focus on logistics not only supports e-commerce growth but also integrates with fintech (faster delivery can encourage more use of payment services like Mercado Pago). In short, Mercado Livre’s logistics optimization in 2025 was a multi-pronged strategy to speed up deliveries, reach more customers, and improve profitability.
- Technological Innovation and Data-Driven Capabilities: Underpinning Mercado Livre’s operations is a relentless focus on technology and data. The company has invested heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to power its platforms. These technologies are deployed across various functions – from personalizing the shopping experience to managing credit risk. In 2025, Mercado Livre’s use of AI helped deliver “smarter recommendations” to users, improving product discovery and conversion rates. Its recommendation engines analyze browsing and purchasing behavior to suggest relevant items, increasing the likelihood of a sale. AI and data science are also employed to “fight fraud at scale” – a critical capability for an e-commerce and fintech platform handling millions of transactions. By leveraging ML models to detect suspicious patterns, Mercado Livre can protect buyers and sellers, thereby building trust in its marketplace. Another area where tech shines is credit underwriting. Mercado Pago’s rapid expansion of its credit portfolio is made possible by robust risk models that use alternative data (like a seller’s marketplace history) to assess creditworthiness. This data-driven approach has allowed Mercado Livre to offer loans and credit cards to millions who were underserved by traditional banks, while keeping default rates manageable. The company’s advertising platform, Mercado Ads, also relies on advanced algorithms to match ads with relevant users, maximizing advertiser ROI and creating a new revenue stream. Beyond AI, Mercado Livre has been investing in cloud computing, big data analytics, and even blockchain technology to bolster its systems. These technological investments have created a highly scalable and efficient platform. For example, during peak shopping events, Mercado Livre’s systems can handle enormous traffic and transaction volumes without significant downtime, thanks to its cloud infrastructure and data management capabilities. In essence, technology is not an afterthought for Mercado Livre – it is core to its strategy. The company’s ability to innovate (whether it’s introducing new digital payment features or deploying robots in warehouses) has kept it at the forefront of e-commerce in Latin America. This technological edge is a critical strength that competitors find hard to replicate quickly.
- Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships: While organic growth has been Mercado Livre’s primary engine, the company has also made strategic acquisitions and partnerships to bolster its offerings. In 2025, Mercado Livre continued to pursue inorganic growth in key areas. One notable move was the acquisition of Pixsa, a Brazilian digital payment startup, to enhance its fintech capabilities. Pixsa’s technology and team were integrated into Mercado Pago, likely strengthening its digital wallet and payment solutions. This acquisition aligned with Mercado Livre’s goal of expanding its financial services ecosystem and staying ahead in the fast-evolving payments landscape. Additionally, Mercado Livre formed partnerships to complement its core business. For instance, it partnered with Google Ad Manager and AdMob to extend the reach of its advertising platform beyond its own marketplace. By leveraging Google’s vast ad network, Mercado Ads can help merchants target customers on a wider scale, turning Mercado Livre into a significant player in the retail media space. Another strategic partnership was with Roku and HBO to introduce connected TV (CTV) advertising inventory. This move allows Mercado Ads to offer premium ad placements on streaming platforms, tapping into the growing CTV market and giving advertisers new ways to engage consumers. These partnerships reflect Mercado Livre’s strategy of integrating its ecosystem with the broader digital advertising ecosystem, thereby increasing its relevance to brands and agencies. In logistics, while much of the expansion has been organic, Mercado Livre has also allied with local specialists in certain cases. An example is its partnership with Casas Bahia (a large Brazilian retailer) to handle logistics for bulky appliances and furniture. This arrangement lets Mercado Livre focus on its strength (small parcel delivery) while leveraging Casas Bahia’s expertise in large-item delivery, effectively filling a capability gap. Such alliances are indicative of Mercado Livre’s pragmatic approach – it builds what it can in-house and partners where it makes sense to speed up service or enter new segments. Overall, Mercado Livre’s acquisition and partnership strategy in 2025 was focused on enhancing its core competencies (payments, advertising, logistics) and expanding its ecosystem’s reach. These moves have made the company’s offerings more comprehensive and harder for competitors to replicate.
- Mercado Pago’s Evolution and Ecosystem Synergy: A critical strategic theme for Mercado Livre has been the deep integration of its e-commerce and fintech businesses. In 2025, this synergy was more pronounced than ever. Mercado Pago, once just a payment processing tool, has evolved into a full-fledged financial services platform. It now offers digital wallets, credit (through Mercado Crédito), a credit card, and even buy-now-pay-later options. The company’s vision is to become the “largest digital bank in Latin America”, and 2025 saw significant progress toward that goal. Mercado Pago’s user base and engagement soared, as discussed, and its products became more embedded in users’ daily lives. For example, many small business owners in Brazil rely on Mercado Pago not just for receiving payments, but also for accessing credit to grow their businesses. This creates a virtuous cycle: as more merchants use Mercado Pago for financial services, they become more dependent on Mercado Livre’s ecosystem, increasing their loyalty to the platform. Meanwhile, consumers who use Mercado Pago’s wallet or credit card are more likely to shop on Mercado Livre’s marketplace due to the convenience and incentives (like instant discounts or cashback). This ecosystem synergy is a powerful strategic advantage that competitors struggle to match. In 2025, Mercado Livre also focused on financial inclusion – offering its services to underserved segments of the population. For instance, in Brazil, over 60% of adults lacked a credit card, and Mercado Pago’s entry into that market with its credit card product addressed a huge gap. By providing credit to those who were previously excluded, Mercado Livre not only grew its fintech business but also deepened its social impact and customer relationships. The company’s fintech strategy is also about long-term monetization – as Mercado Pago gathers more users and transaction data, it can offer more sophisticated financial products and even expand into new areas like insurance or wealth management. In summary, the strategic emphasis on Mercado Pago in 2025 was to transform it from a support function into a growth engine in its own right, one that feeds back into the core commerce business and strengthens the overall ecosystem.
- Omnichannel and Customer-Centric Initiatives: Another facet of Mercado Livre’s strategy in 2025 was the continued push toward omnichannel retail and improving the end-to-end customer experience. While primarily an online player, Mercado Livre has been experimenting with physical presence and hybrid models. It launched its own branded physical stores in select cities (for example, “Meli Stores” in São Paulo) to provide a pickup point for orders and a showroom for certain products. These stores are part of an omnichannel strategy to give customers more flexibility – they can shop online and pick up in-store, or browse in-store and order online for delivery. This approach mirrors trends in global retail and helps Mercado Livre cater to consumer preferences for convenience. Additionally, the company has been enhancing its app and website with features like live streaming shopping and social commerce elements, recognizing that shopping is becoming more entertainment-driven. These initiatives, while still in early stages, show Mercado Livre’s willingness to adapt its model to changing consumer behavior. On the customer service front, Mercado Livre invested in AI chatbots and data analytics to provide 24/7 support and personalize interactions. It also expanded its seller services – offering tools for small and medium businesses to manage their online stores, analyze sales data, and even handle fulfillment through Mercado Envios. By making it easier for sellers to succeed on its platform, Mercado Livre ensures a healthy marketplace with a wide variety of products, which in turn attracts more buyers. In essence, Mercado Livre’s strategy in 2025 was deeply customer-centric: whether it’s faster delivery, easier payments, or more engaging shopping experiences, the goal is to reduce friction and increase value for both buyers and sellers. This focus on the customer has been a key driver of its growth and market position.
In evaluating Mercado Livre’s 2025 strategic moves, one sees a company that is leveraging its strengths (integrated ecosystem, technological prowess) while aggressively addressing any weaknesses. It has invested heavily to shore up logistics and financial inclusion – areas where it saw opportunities to differentiate. It has also pursued partnerships and acquisitions to accelerate its evolution. The net result of these strategies is a stronger, more resilient business model that is well-positioned to capture the ongoing growth of Brazil’s e-commerce market.
However, as with any strategic plan, there are areas that will require continued focus. For example, Mercado Livre will need to ensure that its rapid expansion (especially in logistics and credit) remains sustainable and does not overly strain its finances. It must also keep innovating on the technology front to stay ahead of nimble startups and global tech giants. Overall, Mercado Livre’s strategic assessment for 2025 is largely positive – its initiatives have bolstered its competitive position and set the stage for future growth.
SWOT Analysis of Mercado Livre’s Position in Brazil
To provide a structured evaluation of Mercado Livre’s standing in Brazil, a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is instructive:
Strengths:
- Market Leadership and Scale: Mercado Livre is the undisputed leader in Brazil’s e-commerce market, with the largest customer base and highest market share. This scale gives it significant bargaining power with sellers and suppliers, and it can invest in infrastructure and technology at a level that competitors cannot easily match. Its brand recognition and trust among consumers are major assets.
- Integrated Ecosystem: One of Mercado Livre’s greatest strengths is its uniquely integrated business model, combining e-commerce, digital payments, logistics, and credit services. This creates a seamless experience for users and a network effect that strengthens over time. For example, data from the marketplace can be used to improve credit decisions, and the payment platform can incentivize more shopping on the marketplace. This synergy is difficult for competitors to replicate.
- Logistics and Fulfillment Network: Mercado Livre has built a robust logistics infrastructure (Mercado Envios) that includes fulfillment centers, a last-mile delivery fleet, and even proprietary technology for route optimization. This network allows for faster and more reliable deliveries than many competitors can offer, which is a key competitive differentiator. In Brazil, Mercado Envios handles an estimated 95% of deliveries via its own infrastructure, underscoring its control over the fulfillment process. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also creates cost efficiencies over time.
- Technological Capabilities: The company is a technology powerhouse, leveraging AI, big data, and cloud computing to drive its operations. Its recommendation engines, fraud detection systems, and credit risk models are world-class and give it an edge in personalizing the shopping experience and managing risk. Technology also enables rapid experimentation – Mercado Livre can quickly test new features or business models (such as social commerce or new fintech products) and scale them across its platform.
- Financial Services Growth: Mercado Livre’s fintech arm, Mercado Pago, has become a major strength in its own right. It has grown to have tens of millions of users and a burgeoning credit portfolio. This diversification of revenue reduces Mercado Livre’s reliance on e-commerce transaction fees and adds high-margin financial services revenue. It also deepens customer engagement – users who have a Mercado Pago wallet or credit card are more likely to stick with the platform.
Weaknesses:
- Dependence on the Brazilian Market: A significant portion of Mercado Livre’s business is concentrated in Brazil. While this has been a strength (given Brazil’s large market), it also means the company is exposed to Brazil-specific risks such as economic downturns, regulatory changes, or political instability in that country. If Brazil’s growth slows or if there are adverse policy shifts, Mercado Livre’s performance could be disproportionately impacted.
- Intense Competition and Price Pressure: The competitive landscape in Brazil is fierce, with rivals like Shopee and Amazon undercutting prices and aggressively pursuing customers. This has forced Mercado Livre to sacrifice margins in the short term by offering free shipping and absorbing costs to compete on price. While these moves defend market share, they put pressure on profitability. Sustaining this price competition without eroding the company’s financial health is a challenge.
- Execution Risks of Rapid Expansion: Mercado Livre’s aggressive investments in logistics, credit, and new markets come with execution risks. Rapidly expanding a fulfillment network or launching new financial products can lead to operational hiccups or higher-than-expected costs. For example, opening dozens of new fulfillment centers in a short span requires careful planning and training. Any missteps could result in service quality issues or financial inefficiencies. Similarly, the fast growth of the credit portfolio raises the risk of credit losses if economic conditions sour.
- Brand Perception and Trust: While Mercado Livre is well-known, it faces challenges in certain segments. Some consumers view e-commerce marketplaces (especially third-party ones) with caution regarding product authenticity or seller reliability. Mercado Livre has worked hard to build trust through buyer protection programs and seller verification, but any high-profile fraud or counterfeit incident could undermine that trust. Additionally, as the company expands into fintech, it must ensure that its financial services are perceived as safe and reliable, which is critical for user adoption.
- Operational Complexity: Managing such a broad ecosystem – from retail to payments to logistics to advertising – is inherently complex. There is a risk of internal silos or inefficiencies as different business units grow. Ensuring that all parts of the ecosystem work in harmony (for example, that logistics data informs marketing and finance, or that payment data helps improve marketplace recommendations) is an ongoing operational challenge. Any breakdown in coordination could slow decision-making or innovation.
Opportunities:
- Continued E-Commerce Growth in Latin America: The broader Latin American e-commerce market is still in a growth phase, with plenty of room for expansion. Only about 53% of Latin America’s population is online, meaning as internet penetration increases, e-commerce will likely see a surge in new users. Even in Brazil, e-commerce as a percentage of total retail is lower than in developed markets, indicating untapped potential. Mercado Livre is well-positioned to capture this growth, especially with its logistics and technology advantages.
- Financial Inclusion and Fintech Expansion: There is a massive opportunity to provide financial services to underserved consumers and small businesses. In Brazil alone, tens of millions of people lack access to formal banking services, and many SMEs struggle to get loans. Mercado Pago’s success so far is just the beginning. The company can expand into areas like insurance, wealth management, or even digital banking services (there are reports of plans to launch a digital bank in key markets). By doing so, Mercado Livre can not only grow revenue but also further embed itself in customers’ financial lives.
- Diversification of Revenue Streams: Mercado Livre has been successfully diversifying beyond marketplace transaction fees. The growth of advertising revenue (Mercado Ads) is a prime example – by monetizing its traffic, the company creates a new income stream. There is potential to further expand advertising (for instance, by opening Mercado Ads to third-party advertisers outside the Mercado Livre ecosystem) and even explore other services like streaming media or subscription services. Each new service can reduce reliance on any single revenue source and increase the overall valuation of the company.
- International Expansion: While Brazil and Mexico are currently the largest markets, there are other Latin American countries where e-commerce is still nascent. Mercado Livre has a presence in 18 countries, but it has not fully tapped the potential in many of them. For example, countries like Colombia, Peru, or Chile have growing middle classes and improving internet access. Mercado Livre could invest more in these markets, using its playbook of logistics and fintech integration, to capture new customer bases. Additionally, there could be opportunities for strategic partnerships or acquisitions in other regions to accelerate growth.
- Partnerships with Traditional Retailers: As e-commerce and retail converge, there is an opportunity for Mercado Livre to partner with or acquire traditional brick-and-mortar retailers. Many retailers in Latin America are looking to digitize but lack the expertise. Mercado Livre could offer its platform and services to these retailers, effectively becoming a technology and logistics provider for them. This would instantly expand its reach and user base without Mercado Livre having to acquire customers from scratch. It’s a model that has been explored in some markets (for instance, Mercado Livre’s partnership with Casas Bahia for large appliances) and could be replicated elsewhere.
Threats:
- Intensifying Competition: The competitive threats to Mercado Livre are multifaceted. Global giants like Amazon are continuing to invest in Latin America and could become more formidable if they gain traction. Asian platforms like Shopee, AliExpress, and now Temu have shown they can quickly win over price-sensitive consumers, potentially eroding Mercado Livre’s market share. Even regional players like Magazine Luiza are investing heavily in online capabilities. The threat is not just from one company but from the overall competitive environment, which is pressuring Mercado Livre to spend more on marketing, discounts, and infrastructure.
- Regulatory and Government Policy Risks: Mercado Livre operates in a complex regulatory landscape across Latin America. Changes in laws or government policies could pose significant challenges. For example, data privacy regulations (such as Brazil’s LGPD) require strict compliance and can limit how the company uses customer data. There is also the risk of antitrust or competition law scrutiny – Mercado Livre’s dominant position in Brazil could attract regulatory attention, potentially leading to restrictions on its business practices (as has happened with other tech giants in various countries). Additionally, changes in import/export policies or tax laws could affect cross-border commerce, which is a growing segment. Any protectionist measures (for instance, higher tariffs on imports) could hurt Mercado Livre’s ability to offer a wide range of products at competitive prices.
- Economic and Currency Volatility: Many Latin American economies are prone to economic volatility and currency fluctuations. Mercado Livre’s revenue and costs are spread across multiple countries with different currencies, making it sensitive to exchange rate movements. A significant devaluation of a local currency (like the Brazilian real or Argentine peso) against the dollar can hurt the company’s financial results when consolidated. Moreover, economic downturns or high inflation in key markets could reduce consumer spending power, dampening e-commerce growth. The company has to manage these risks through financial hedging and by diversifying its revenue streams, but they remain a constant background threat.
- Cybersecurity and Fraud Risks: As a digital platform handling vast amounts of customer data and financial transactions, Mercado Livre is a target for cyberattacks and fraud. A major security breach or a large-scale fraud incident could erode trust in the platform and lead to financial losses. While Mercado Livre invests in cybersecurity and fraud prevention, the threat landscape is always evolving. Any lapse in security could have serious consequences, including regulatory fines and loss of customers.
- Technology Disruptions: The rapid pace of technological change means that new disruptive technologies or business models could emerge that threaten Mercado Livre’s position. For instance, advancements in AI by competitors or new platforms could make Mercado Livre’s offerings seem dated. There is also the threat of blockchain-based marketplaces or decentralized e-commerce models that bypass traditional intermediaries. While these are still nascent, Mercado Livre must stay at the forefront of tech innovation to ensure it isn’t caught off guard by a paradigm shift in how e-commerce is conducted.
In summary, Mercado Livre’s SWOT analysis paints a picture of a company with formidable strengths (market leadership, integrated ecosystem, technology prowess) that is capitalizing on major opportunities (e-commerce growth, fintech expansion). However, it must also carefully navigate weaknesses (dependence on Brazil, execution risks of expansion) and guard against external threats (intense competition, regulatory risks). The company’s strategic initiatives in 2025 were clearly aimed at leveraging its strengths and opportunities while mitigating the weaknesses and threats. Going forward, maintaining this balance will be crucial for sustaining its leadership position.
Conclusion
Mercado Livre’s performance in 2025 has been nothing short of impressive. In the dynamic Brazilian market, it not only defended its leading position but also expanded its reach and influence. The company’s financial results – surging revenues, strong profits, and record GMV – underscore the effectiveness of its strategies. Its ability to grow its user base, especially unique buyers, at the fastest pace in years is a testament to the appeal of its platform and ecosystem. The investments in logistics have paid off in faster deliveries and better customer experiences, while the fintech arm’s rapid growth has opened new avenues for revenue and customer engagement.
Equally important, Mercado Livre has proven that it can adapt and innovate in the face of competition. Whether it’s matching Shopee’s aggressive shipping offers, expanding its advertising business, or rolling out new financial products, the company has shown agility and determination. Its integrated business model, blending e-commerce, payments, and logistics, continues to be a potent competitive advantage that is hard for rivals to replicate. This ecosystem approach not only differentiates Mercado Livre in the market but also creates a sticky user experience that should benefit long-term growth.
Looking ahead, the opportunities for Mercado Livre are vast. Brazil’s e-commerce market is expected to continue growing at a double-digit clip, and Latin America’s overall digital economy is still in its early stages. By leveraging its strengths and learning from the challenges of 2025, Mercado Livre is well-positioned to capture a significant share of this future growth. The company’s focus on technology, customer satisfaction, and ecosystem expansion provides a solid foundation for the next phase of its journey.
In conclusion, Mercado Livre’s 2025 performance in Brazil has been a triumph. It has managed to grow faster than the market, outpace competitors, and execute on a bold strategic vision. The result is a stronger, more resilient company that is leading Latin America’s e-commerce evolution.
As the region’s digital economy matures, Mercado Livre is poised to remain at the forefront, driving innovation and delivering value to consumers, entrepreneurs, and investors alike. Its story in 2025 is one of strategic clarity and operational excellence, and it sets the stage for what could be an even more promising future. For Brazil and Latin America, Mercado Livre’s success is not just a business success story – it is a catalyst for economic growth and inclusion, empowering millions of sellers and buyers to participate in the digital marketplace. The journey is far from over, but if 2025 is any indication, Mercado Livre is on the right path to continued leadership and impact in the years to come.
Temu vs. Shein: Which App is Safer
By langxu freight | Updated: 2026 The battle for the top spot in the ultra-fast…
Mastering the Ocean Bill of Lading
In the fast-paced world of international logistics, cargo moves across oceans, but paperwork rules the…
e-commerce How to Secure Your Supply Chain and Amplify Your Brand
Your shop is growing. The adrenaline of the first few sales has settled into a…