CNF shipping explained simply: It’s Cost and Freight. The seller covers costs and freight to get goods to the destination port. Learn your responsibilities now!
Do you know what is CNF meaning and how it can help you save costs in shipping?
what is CNF Shipping Term
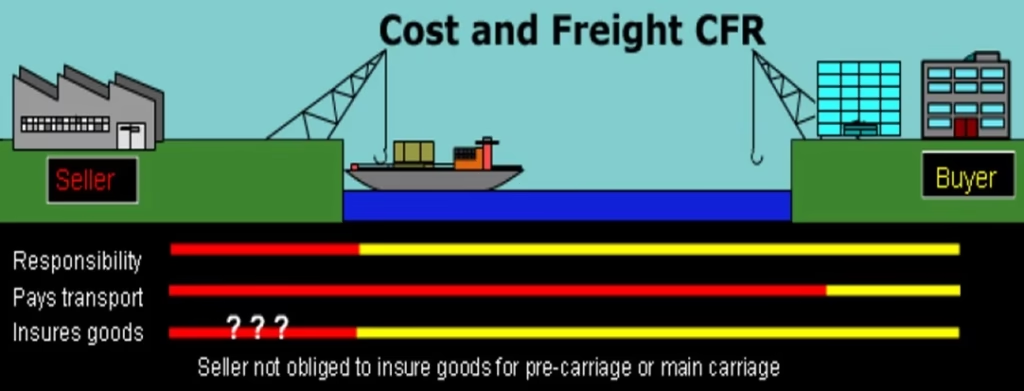
CNF stands for Cost and Freight; It is a legal term that is commonly used in international shipping and transportation.
CNF refers to a shipping agreement between a buyer and a seller in which the seller pays to send the item to a destination port to the customer, and the buyer is responsible for the rest of the shipping charges from the port to the buyer’s destination or warehouse.
1: Overview of CNF & Common Concepts
Global trade needs a clear process for products crossing borders. It includes contracts, transport, and moving items to buyers. Incoterms are vital for clarity in this process. The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) makes these terms. Incoterms define each party’s duties during shipping. They ensure smoother transactions and avoid confusion.
1. CNF Meaning
CNF, short for Cost and Freight, is among the Incoterms that define what the seller and buyer need to do during shipping.
It consists of three key parts:
Cost: This is the amount the buyer pays for the goods being shipped.
Insurance: This covers any potential loss or damage while the goods are in transit. In CNF, the buyer is responsible for arranging insurance.
Freight: This is the expense of moving the goods from where the seller is located to the destination port.
2. What is CNF? Is CNF, C&F and CFR the same?
Cost and Freight, also called CFR or C&F, is a shipping contract. This agreement is between a seller and a buyer for shipment costs. This term applies only to sea freight. The seller pays to get items to the buyer’s closest port. From there, the buyer covers all shipping fees. Remember, CNF, C&F, and CFR mean the same thing. There is no difference in how they work. C&F and CFR are common in both local and global trade. Some people also use CNF.
3. The Usage of CNF Incoterm
When and who should use this incoterm?
It’s important to understand when to use the CNF Incoterm to get the most benefit. Let’s look at the scenarios where using CNF is the best option:
Sea Freight Shipments
CNF shipping term is commonly used for shipments that travel via sea route.
Experienced Importers
This Incoterm is suitable for experienced buyers who understand the import processes and can manage customs clearance and delivery from the port onward.
Price-Sensitive Markets
The CNF shipping term can also benefit sellers targeting price-sensitive markets. It allows them to offer competitive prices for the goods that include freight costs.
For example, a seller in China is exporting electronics to a buyer in the US. By using the CNF shipping term, the seller includes the cost of shipping the goods by sea to the port in the US. It will allow the seller to offer a more competitive price for the electronics, as the buyer doesn’t need to worry about covering the freight costs separately. However, the buyer will still be responsible for customs duties and delivery from the port. This makes the offer more attractive to price-sensitive buyers in the US.
4. Relevance of CNF and incoterms
Incoterms is a short form of International Commercial Terms. Incoterms are commercial universal terms that are standardized to help and aid the trade.
They include 11 predefined sets of rules and regulations for buyers and sellers to facilitate international trade. CNF is one of the eleven pre-defined and globally recognized incoterm.
The main purpose of defining these terminologies is to specify centralized, authentic, and constant standards for international trading.
With the help of CNF, buyers and sellers can get a better understanding of risks, tasks, costs, and tax-related information that can be involved in transferring the goods.
These terminologies are usually used by people who are involved in the overseas delivery of goods including buyers, sellers, producers, banks, and traders use these terminologies.
5. Is CNF applicable to all modes of transportation?
Choose CNF when your goods travel by sea! Other Incoterms like CIF and FOB also work for sea or air cargo. But don’t forget: other Incoterms exist for different ways to ship. So, explore your options to find the perfect fit!
6. What are the Benefits of CNF for Sellers and Buyers?
The CNF (Cost and Freight) shipping term offers several benefits to both sellers and buyers. It simplifies the shipping process by clarifying responsibilities and costs. The table below shows the benefits of CNF for sellers and buyers:
| Benefits for Sellers | Benefits for Buyers |
| Clear cost structure up to the port of destination. | Control over the import process, as they can choose custom brokers and insurance providers of their choice. |
| Simplified logistics as they only need to arrange transportation to the destination port. | Flexibility in transportation from the port. They can choose their preferred mode of transportation from the port onwards. |
| They can offer their goods at competitive rates to reach more buyers. | They can choose their favored insurance providers and save on insurance costs. |
7. What are the Drawbacks of CNF for Sellers and Buyers?
Although CNF has its benefits, we cannot deny its drawbacks. These challenges come from the way costs and responsibilities are split between sellers and buyers. You should acknowledge these issues before a trade to decide if CNF is the best choice for you.
Let’s understand how the CNF Incoterm can be unfavorable for sellers and buyers.
| Drawbacks for Sellers | Drawbacks for Buyers |
| Sellers do not have control over the delivery once the goods are on the ship. | Buyers must handle all the customs and import paperwork, which can be time-consuming |
| If there are delays in customs, it may impact when the seller receives payment. | After delivery, buyers are responsible for any loss or damage to the goods. |
| Sellers are responsible for any damage that occurs during unloading at the destination port. | Buyers may need to pay higher insurance costs, as they are responsible for insuring the goods after delivery. |
8. What is the difference between CNF and CIF?
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) shares traits with CNF, which causes confusion. Both require the seller to unload goods at the port nearest the buyer. The buyer then handles customs and cargo delivery to its final place. CIF goes further: sellers must insure the goods. This means the supplier or seller is responsible for any damage during shipment. Choose CIF for secure delivery.
How to Calculate CNF Pricing Accurately?
Before calculating CNF pricing, grasp the costs involved. Sellers pay CNF charges. However, buyers also cover some costs outside the CNF shipping term.
Buyers must know CNF inclusions and separate costs. This clarifies who pays for what and avoids surprises.
Let’s break down CNF costs. We’ll also explore costs not covered by CNF shipping.
Costs Included in CNF
Here is the list of the costs that are included in the CNF price. The seller pays for all costs until the goods reach the destination port. These include:
- Export fees
- Shipping charges
- Packing, labeling, and loading the goods onto the ship
- Getting export approvals, like licenses and permits
Costs Not Included in CNF
CNF can be a cost-effective choice as it covers freight and shipping charges. However, some costs are not included and need to be paid separately by the buyers.
Here is a list of shipping costs not covered under CNF (Cost and Freight).
- Unloading costs
- Import duties
- Taxes
- Insuring the goods during transit
- Customs clearance fee
- Port charges
- VAT (value-added tax)
- Docking charge
- Warehouse storage fee
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating CNF Pricing
CNF pricing includes the cost of goods and freight charges to the destination port. However, buyers must also consider additional expenses incurred after the shipment arrives.
Initial CNF Price
At the time of calculating CNF pricing, first consider the seller’s price. This includes the cost of the goods and the shipping charges to deliver the goods to the destination port.
Add Additional Charges
After the goods arrive, include costs like customs duties, import taxes, and port handling fees.
Calculate the Final Total
Add the initial CNF price and the additional charges to get the total cost of the shipment.
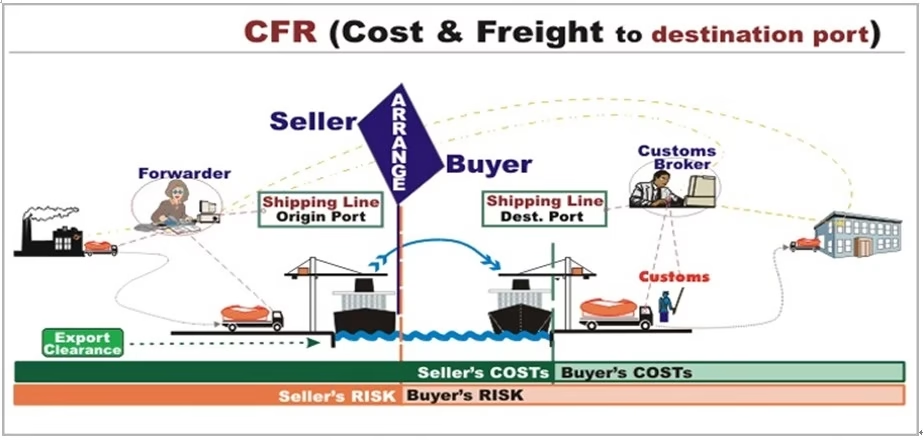
Responsibilities of Buyer and Seller in CNF Incoterm
As noted, CNF helps both sellers and buyers figure out cargo costs. It also helps with shipping fees. Now, let’s explore buyer and seller duties. We will show what each party must do. Learn how CNF protects your interests.
1. In CNF (Cost and freight) shipping, what are the major Seller’s responsibilities?
Following is the list of common responsibilities of seller in a CNG agreement.
- Goods invoice and documentation
An invoice is a commercial document, and it includes all the charges and details on the account of the goods that are being shipped.
It can have information regarding terms and methods of payment. According to CNF term, preparing the invoices of the goods and all other necessary documentation is the seller’s responsibility
- Packaging and marking
Goods are packed and marked before shipment to keep them safe and protected. In CNF (cost and freight) seller is responsible for the packaging and marking of products before shipment.
- Fulfilling Customs formalities
In CNF Seller is also responsible to take care of all the customs formalities before shipping the cargo. Clearing all the customs formalities is necessary for the international shipments.
- Delivery and Pre carriage
Pre carriage is an inland movement of the cargo before the container is being loaded or moved to the port or terminal. In CNF, the seller is responsible for the delivery and pre-carriage activates and the seller is also responsible for all the delivery and pre-carriage fees or charges.
- Loading fees
The loading fees refer to the fee of loading the containers to the ocean vessel for the delivery of the goods. In CNF, the seller is responsible for the payment of the loading fee.
- Delivery at the port
The final activity of the seller is the delivery of the goods to the port that is nearest to the buyer. Seller responsibility ends here, and the buyer is responsible for the activities that take place afterward like delivery of the goods from port to the buyer’s place.
2. In CNF (Cost and freight) shipping, what are the major Buyer’s responsibilities?
- Payment for goods
The buyer needs to make the payment of the received goods. All the payments should be cleared and payment should be made according to the pre-decided terms and conditions.
- Discharge and forward carriage
According to CNF, Once the seller ship the goods to the nearest port, the buyer needs to discharge and forward the carriage from that point onward.
- Is there a formula to estimate the CNF final price for Buyer or Seller?
There is no formula available to estimate the final CNF price. Buyers and sellers can calculate the price roughly by considering all their expenses.
However, it is important to keep in mind the final CNF price will be always greater than the estimated price because of the extra additional charges of delivery and customs clearance.
How Freight Forwarding Agent can Help with your Shipments from China?
1. Cost overhead in the CNF(Cost and Freight) price can be minimized
In the CNF agreement, there are a lot of additional costs that are not included in the CNF cost, and the buyer or seller needs to bear that costs. Using a freight forwarding agent can help in minimizing the cost overhead in the CNF.
2. Freight Forwarding Agent provide cost-effective services
Freight forwarding companies usually deal with the goods in bulk volume. It is easier for them to negotiate a better price with carriers due to bulk volume.
There are a lot of freight forwarding agents in China that offer competitive prices for managing all the services whose costs are not included in the CNF such as warehouse service and customs clearance etc.
3. Freight forwarder simplifies the Shipping process
If you are a beginner in trading then managing all these trading-related responsibilities can be overwhelming for you. A freight forwarding agent simplifies the whole shipping process.
Taking the service of a trustworthy freight forwarding agent, you won’t have to invest your time and energy in comparing the prices, researching, and negotiating.
4. Freight Forwarding Agents are trustworthy and reliable
Freight Forwarding Agents are trustworthy and reliable. All the processes that are included in the shipping from the seller’s side to the buyer’s end are documented properly to maintain the quality and control check. Chinese companies & Agents provide reliable and competitive services.
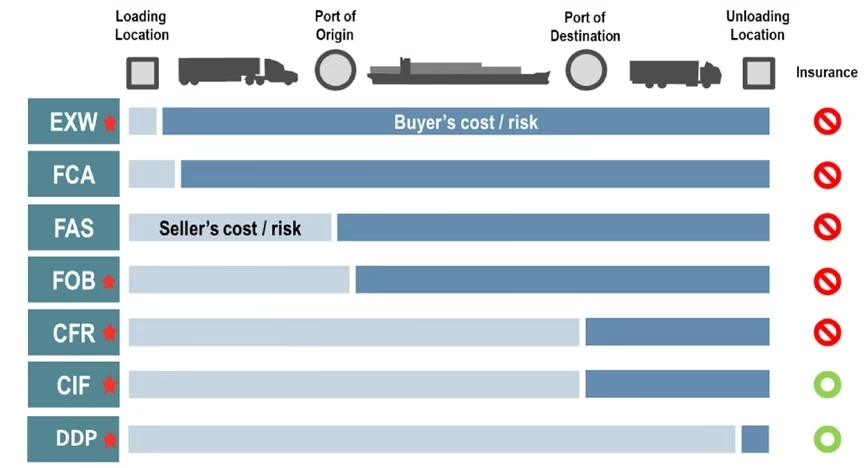
Difference between CNF and other Shipping Terms?
Some other incoterms have some similarities with the CNF, but they are different. In this chapter, we have provided a brief comparison between CNF and some other well-known incoterms.
1. CNF vs FOB
FOB, or Freight on Board, defines shipping responsibilities. With FOB Destination, the seller ensures safe delivery to the supplier’s destination port. The shipper covers any damage during this transport. FOB Shipping Point shifts responsibility. Here, the shipper only gets the goods to the shipping port. The buyer then takes over for the ocean voyage. The agreed terms dictate who bears the risk.
CNF terms make the shipper liable for losses until cargo unloading. Shippers and buyers agree on these terms upfront. For small shipments, CNF is often best, especially for new traders. Experienced international traders with established logistics often prefer FOB. With FOB, you have more control.

2. CNF vs EXW
Ex Works, or EXW, puts all shipping duties on the buyer. This benefits the seller, who avoids shipping costs.
For instance, a Chinese seller and a UK buyer agree to EXW. The seller readies the shipment. The buyer then picks up the cargo in China.
The buyer is fully responsible for the entire shipment. The seller is not liable for any damage. Any losses during shipping are the buyer’s burden.
CNF agreements differ. Both the seller and buyer share shipping duties under CNF terms.
3. CNF vs DDP
Delivered Duty Paid, or DDP, places all shipping duties on the seller. The seller remains responsible until the buyer receives the cargo.
The seller handles all shipping tasks, covering potential losses or damages. They also pay all transport costs, including insurance and customs.
Sellers must deliver goods to the buyer’s agreed destination. DDP favors buyers, as sellers handle most shipping tasks and costs.
The seller delivers the customs-cleared goods to the buyer’s warehouse. CNF, by comparison, splits shipping duties and costs between seller and buyer.
4.CNF vs CIF
Cost, Insurance, and Freight is known as CIF. CIF and CNF share similarities, but they differ. Both operate the same way, but CIF covers cargo insurance.
Imagine a seller in China shipping to a buyer in the USA. The seller pays freight and insurance to the buyer’s closest port.
The seller covers costs until unloading. Then, the buyer gets the cargo. The buyer pays for customs and taxes.
The buyer handles the shipment from the port to their location. CNF mirrors CIF, but CNF excludes insurance. Opt for CIF to protect your shipment!
FAQs about CNF Shipping Term
Can CNF shipment be used for Airfreight?
No CNF incoterm cannot be used for the airfreight. CNF shipment term is only valid for the ocean freight, shipments that are made through the waterway.
Does CNF involve risk?
CNF does not include the insurance cost. In the CNF agreement seller is not responsible for the insurance of the cargo so if the seller or buyer is not taking separate insurance services then it can be risky if any losses or damage occurs during the shipment or loading and unloading of the cargo.
Which Incoterms are best for a seller?
FOB (Freight on Board) is most commonly used in international trade. In FOB seller is responsible for the loading of the cargo on the vessel.
EXW incoterm is most benefitical for the supplier as he just need to make the products and then the buyer will have to collect it from the supplier’s factory or warehouse and handle everything from there.
Which Incoterms are best for a buyer?
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) incoterm is also widely used, this is fully beneficial for the buyer because the seller is responsible to not only ship the goods to the buyer’s country but also clear the goods from the customs and deliver it to the buyer’s warehouse in his own country.
Does CNF include the cost of insurance?
No, CNF does not include the cost of insurance. Seller is not liable to take insurance services for the cargo.
Who does the CNF customs clearance?
These costs include ocean freight, land freight, port charges, etc. In a CNF contract, the seller needs to bear the above two costs. Once the goods arrive at the destination port, the buyer is responsible for customs clearance and paying all fees and taxes related to the import of the goods.
Langxu Freight is one of the more famous freight forwarding companies in China.If you need to purchase any goods in China, or are ready to start an e-commerce business/dropshipping business, let us give you the greatest help. If you need to purchase goods in China, we can provide you with comprehensive freight forwarding services, including quality supplier selection, product quality inspection, free warehousing in China, customs declaration, a variety of reliable and safe transportation plans, and on-time delivery services.





Pingback: 10 knowledge points about cargo fumigation
Pingback: Essential Maritime Shipping Terms